- The most important piece of information is ‘Everybody has something of value to a hacker’. If you’re a one-man band or the biggest business in the world, hackers will always find something of value.
- A massive 78% of burglars say they check Facebook and Twitter for potential targets. Never share your location!
- Tickets to events are one of the most targeted purchases for cyber criminals. Fake ticket scams cost victims £365 on average with Wimbledon and Glastonbury being popular scams. Always check where you’re buying your tickets from and never buy from ticket touts.
- Update, update, UPDATE! We know how annoying it is seeing a pop-up computer, software or application update. But we cannot stress how important it is to always run the latest updates on your computer and smart devices.
- Did you know? 99% of computers are vulnerable to exploit kits. Old software will always be more vulnerable that the most up to date software.
- There are usually four stages to a cyber-attack
1. Survey
2. Delivery
3. Breach
4. Affect
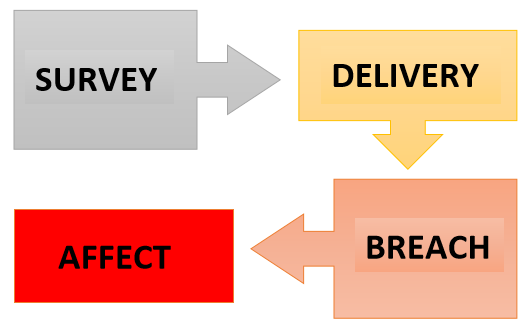
Survey - This is where the attacker will scan and look for potential vulnerabilities in networks or users’ devices.
Delivery – Once a vulnerability has been found this is where the attacker will deliver the virus or malware. Delivering a virus can be done via phishing emails or fake websites.
Breach – If the virus or malware is delivered to the intended device the attack then enters the breach phrase. Attackers can then start making changes to your system.
Affect – This is the final part of an attack. If an attack reaches this stage attackers can edit data and also leave a permanent access route on your network.
It’s possible for you to find an attack at any of these stages but it’s also possible for attacks to go through all four of these stages without being noticed.
- The biggest cause of poor cybersecurity is human error. While computers get smarter and smarter, people are still making the same fundamental errors when it comes to cybersecurity.
- Your cyber security is only as strong as the weakest or least trained person using the network. If you work in a business make sure everybody has at least a basic understanding of cybersecurity.
- Did you know that 267 million records were breached in the UK during September 2020 alone due to cyber attacks and data breaches.
- Let’s bust five common myths when it comes to cybersecurity.
'It will never happen to me; I won’t get attacked’.
Everybody at some point will be a target for a cyber criminal. Your defences will determine how easy it is for the cyber criminal to get into your system.
'Implementing cyber-security costs too much money and takes too much time’.
If you change even just one security setting for the better, you’ll instantly become more secure. A lot of the methods mentioned in this guide can be done completely free and take no longer than 10 minutes.
‘I only ever buy from trusted websites my data will never get breached’.
While it’s encouraged to use trusted websites, it never means your data will be 100% safe. Amazon, Google, eBay and many more of the worlds most used sites have all suffered from data breaches in the past.
‘If I get hit by an attack my computer will alert me, and I’ll be able to fix it’. Firstly, an attack could happen, and you may have no idea. Secondly, even if your computer alerts you that an attack has taken place, it doesn’t mean you’ll be able to fix it.
‘Nobody will be able to guess my password they don’t know me that well’. A recent report stated that 90% of passwords could get cracked in 6 hours or less by cyber-criminals. Any personal information in a password is a big no.
- While most attacks are carried out over the web, another method is also to infect USB devices that can be plugged into a computer. Always check before you plug in. Do you know where it come from and what is on the device?
- The term antivirus has been around for years, and it may seem a little outdated, but it’s still important to have on your devices. Both your computer and mobile phone should have some form of antivirus installed.
- Back up a second. You should always have a full backup of your data. You can get software that will automatically back your data up at regular times. We recommend doing this to an external hard drive. If your computer or device comes infected, you then have a copy of uncorrupted data.
- There are two types of cyber attacks, targeted and non-targeted. Targeted attacks will go after specific users or businesses. Non-targeted attacks will cast a large net over the web and look for any vulnerable networks or systems.
- Ransomware can be a targeted or non-targeted attack. This is where a user will get locked out of their device and attackers will usually demand a fee for the data to be given back.
- If you’re unfortunate enough to suffer from a ransomware attack, you should never pay the money. Even if you meet their demands, there’s no guarantee you’ll get the money back. Therefore, you should keep a backup of your data.
- Get a paper shredder. You’re right in thinking this is a guide about online security but any important paper documents that you no longer need should be shredded. If these documents fall into the wrong hands, they can be used to compromise your online security.
- Do you use the webcam on your laptop? If you answered no, then tape over it. This may make you look a little paranoid, but it’s a logical way of being more secure. Even Facebook’s owner does it!
- Did you know that UK businesses lose £27 billion to cyber-attacks every year.
- Use Google Analytics to check where traffic is coming to your website (if you have one). If you do have a website, it’s good to know where in the world traffic is coming from. This data can also help if you are subject to a cyber attack.
- Did you know that the projected cost of cyber-attacks globally is a whopping $575 billion.
Passwords

- Does your device or application give you the option to have a password? Always set one! You wouldn’t leave your front door unlocked overnight. Well, we hope you wouldn’t! Take a look at our password guide for more help.
- One of the easiest and most effective cyber security tips to implement is to look at the passwords you use online. Are there two the same? If so change one of them immediately! Never use the same password for two different accounts.
- These are the five most commonly used passwords online. If you use any of these, we cannot stress how important it is to change them this second!
password
123456
12345678
1234
qwerty
- Make sure your passwords have at least eight characters and are a mix of numbers, letters, lowercase and uppercase. Make them as complex as possible and never have personal information inside them.
- "But how on earth will I remember all these complex passwords?”. The truth is it’s impossible. That’s why we recommend using an online password manager. LastPass is by far our favourite! These online applications will help you create secure passwords and store them for you.
- Implement a password policy that requires you to change your primary login into your device every 90 days. Keeping your passwords fresh helps maintain a higher level of cyber security.
- This may seem a simple one, but people still do it! Do not leave your passwords wrote down next to your computer. Would you have your pin number stuck to your bank card?
SOCIAL MEDIA

- Speaking of leaving your front door unlocked, think twice before checking in on Facebook. Sure, you want to tell your 362 friends you’re off to Spain for two weeks but at the same time you’re also saying “Hey everyone I won’t be in the country for a fortnight, so feel free to pop around to my empty house!”.
- One of people’s biggest downfalls when it comes to cybersecurity is social media. Always review everything before you post it. Does it contain any personal information? If your social media post does involve personal information, delete it.

- Do your social media accounts need to be public? Most social media platforms come with an option to make your account private letting you filter through friends and follow requests. Never accept a request from somebody you don’t know.
- By far the most popular social media platform is Facebook but do you know about its login alerts? When your account gets accessed from a new device, you can be prompted via Facebook, e-mail or text to alert you. If it’s just you on a new device, you can disregard the warning.

- Following on from login alerts It’s also worth activating login approvals. When accessing Facebook from a new device, you will be required to enter a code that’s sent to you via text message. If anybody compromises your account, this extra layer of security known as two-factor authentication (more on that later) will make it even harder for hackers to access your data.
- Facebook’s privacy settings let you control who can see your posts. For most people, you will want to have this set to just friends. This stops unwanted people from seeing your posts on your Facebook page.
- Limit who can send your friend requests. This will stop a lot of spammers who have no mutual friends with you from sending you friend requests. The best option is only to allow who have mutual friends with you to send friend requests.
- In Facebooks settings you can change a host of things such as blocking accounts, controlling third party apps, who can post on your timeline and much more. Take a look at your Facebook settings to make sure you’re secure as possible.
- Being the most popular social media platform in the world, you may think that it’s only important you secure Facebook. It’s also important to implement security across all your social media accounts.
- Even though LinkedIn is seen as the most professional social media platform that doesn’t make it immune to cyber-attacks. It’s reported that an attack that took place in 2012 saw the details of around 117 million LinkedIn users compromised. Attacks can happen anytime, anywhere.

- Sticking with LinkedIn, remember this is probably the account where you share the most information about your workplace. Always review what you share and never put anything too personal out into the public eye.
- Only ever connect with people you know on LinkedIn. Would you tell a stranger on the street where you work what you do and further information? We hope not! Don’t connect with strangers!
- Finally, on LinkedIn, you’re able to request an archive of your data allowing you to see what data you’ve made available for others to see.
- Twitter is one of the more complicated social media platforms to be cyber secure on. One of the first steps you can take is to make your profile private. This allows you to pick and choose who follows your account.

- Go back in time. Inside your Twitter settings, there’s an option to download all your old tweets in an excel file. If any contain sensitive or personal information, make sure you go and delete them off your account.
- Under security and privacy in your Twitter settings, there is an option to turn off the location from your tweets. Make sure you do this and delete all the information from previous tweets at the same time. There’s never a reason to broadcast where you are on social media.
- Twitter is also one of the most popular platforms for phishing attempts. Usually done via direct spam messages, these attacks will try to get you to click a link then affect your account. From here the attackers can automatically tweet out on your account to get others to fall for it. Always check the sender of messages and never click rogue links.
- Moving on to Instagram, like Twitter making your account private is one of the best steps you can take in being cyber-secure on Instagram. You can then choose who sees your photos.
- Geotagging can get out of here. Share where you’ve been and show off the great things you’ve done but wait till you’re at home. Don’t let a stranger follow your every move.
- Always think before you post a photo. Could be anything in the background a rouge letter or email containing personal information could easily find its way into your Instagram post.
Email

- Let’s talk email. Email is easily one of the most important things to protect. If somebody gains access to your emails, consider all of the other accounts they will have access too. Social media, online shopping and more. Make your email password a very strong one.
- Let’s bust a cyber security myth. It’s extremely unlikely for you to get a virus from simply opening an email. Most email providers now have measures in place to alert you to any potential viruses inside the email. Most of the time you will be okay to open the email but if you have any doubts, delete it before opening.
- What about the contents of the email? Attachments are a regular feature in emails, and you must always be alert when you receive one. Even if you’re expecting an attachment in an email be alert and never click attachments you’re not expecting.
- Avoid links in emails at all costs. This is one of the top methods that hackers will you use to infect your device. If you’re unsure about a link, do not click it. Go to a search engine and type in the site manually. No copy and pasting!
- Return to the sender? Not if you don’t like the look of their email address. Always check the address of the send. Their name may look legitimate, but the email address will soon override this. Below is an example of an illegitimate email address:

- Don’t be caught by the bait of phishing. Phishing emails are obvious scams they usually try to convince you to provide your bank account details due to a problem with a payment or a win of millions. If it sounds too good to be true, then it probably is. If you have an email about a missed payment contact the company in question directly via their number from Google or verified social pages.
- Create separate email accounts for home and work. Not only will it stop the risk of mixing professional and social emails but it also allows an extra layer of security. If you keep all your emails in one account if that account is breached everything becomes accessible. Don’t put all your eggs in one basket.
- Look at email security services which will check your emails for you and quarantine any suspicious looking ones. You can then release these emails if you believe they are legitimate. These email security services work great for businesses.
- If you are going away, never share too much information on your out of office notifications. You only need to put the basics of when you’ll be back in the office and an emergency contact number.
Wi-Fi and browsing

- What about if you’re out in public? Do you need to connect to that unprotected Wi-Fi network to Instagram your cappuccino in your favourite coffee shop? Always treat any public Wi-Fi points with caution and question if you need it.
- Forget that network! If you have used a Wi-Fi network that you know you won’t be using again in the near future, make sure you forget it from your device. This will stop you automatically connecting to it if you’re just passing in the range of the network later.
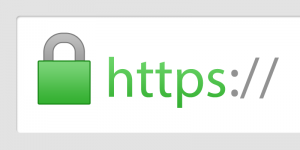
- Keep it green and locked down. You’ve probably seen a little green lock next to a website with the letters HTTPS. HTTPS sites will encrypt data making them much safer to use. This is important on any device and never provide any personal details to a site that doesn’t have HTTPS.
- If you are away on holiday or out and about NEVER use a public computer except for the most extreme times. It’s so easy for criminals to infect these with malware and more.
- How annoying are those ads that regularly pop up while you’re online? You should never click pop up ads as this is a popular way for cyber-criminals to infect devices.
- One of the best ways to avoid these is by installing an ad-blocker on your computer. This will stop the ads from popping up and alert you to any that have been blocked.
- Torrent downloads are still dangerous. In the mid-2000’s torrent downloads were hugely popular. Without so much talk of cyber security back then there were a huge number of viruses in these torrent downloads. Even with better cyber security now torrent downloads are still dangerous.
- Do you think a website is down? Are you worried you’ve been part of an attack? Check if a website is working as it should be at; down for everybody or just me. If it’s just you, not able to access a website, your network may be having trouble.
- When at home make sure you’ve changed the name of your Wi-Fi. You can get a little creative or even make it funny. Changing the name makes it a little harder for cyber-criminals to check what router you’re using.
- Also with your home or business Wi-Fi ensure that you have changed the password from the default one. More advanced cyber-criminals will have a pretty good idea of default Wi-Fi passwords making them easier to hack into.
- If you know you’re going on holiday and nobody will be home for a week, or two make sure you disconnect your Wi-Fi router.
Mobile

- When you’re out and about you’re likely to be using your mobile or tablet device. Make sure your device is up today and running the latest operating system. You’ll usually find any available updates in your settings, make sure you have the latest update.
- The previous rules also apply for mobile applications. While there may seem more important things to do than spending time updating your apps, it’s very important. Application updates can provide better security implemented in the app or patch previous vulnerabilities.
- Auto-locking is essential. Your device will come with a feature usually found in settings that will lock your device after a certain length of inactivity. This is important in case you ever have your device stolen or lose it.
- Do you need bluetooth and Wi-Fi on? If you’re not using bluetooth or Wi-Fi features on your phone, then turn them off. This will increase your security and will reduce the chances of rogue devices connecting to yours.

- Only download apps from trusted places. Use your devices built in app store and never download rogue apps from the internet as they can contain malware and more.
- All these applications and social media platforms are great to lose, but they’re impossible to use if your phone is lost or stolen. Make sure you’ve activated a remote device locator on your smart device. If your phone falls into the wrong hands this bit of security should help you track it down.
- What if you’re selling your phone or sticking in the draw as a backup for your new one? Make sure you factory reset it. A factory reset will wipe any data on the phone and effectively put it back into a new state. This is essential if you’re selling your phone.
- Stick to your own devices. We’ve all been in the situation where we’ve asked to use a friends’ device to log into your favourite site and check something quickly, but do you know how conscious they are about cyber security? Stick to your devices.
- When ending your session on a computer or phone make sure you’re logged out of any websites that you had running and that you shut down your computer correctly when you’re finished using it.
Shopping and Banking

-
How great is online shopping? Order it one day it’s on your doorstep the next, yet this is some cyber criminals favourite playground. Always make sure you’re buying from a reputable site. Check a website’s about page and contact details and always look for the green lock we mentioned earlier.
-
Make sure your payments are secure. If you click the green SSL lock at the top of a web page (if it has one, if it doesn’t do not send any money via that site!), then details you’re able to see a site’s SSL certificate including the dates it was issued.
-
Whenever you buy something online check your online banking straight after. Make sure everything is as it should be and the right amount has been withdrawn from your account. The quicker you spot any errors, the quicker you can act on them.
-
Once you’ve finished online shopping always make sure you log out of your account. There’s never any reason to stay logged in once you have finished your shopping.
.
-
Not only should you try to verify the website but also check the seller. Check customer reviews and make sure you have contact details for them in case anything goes wrong. Never buy from an unverified seller. You wouldn’t give your card details to a stranger on the street.
-
Always read the terms and conditions! We know they’re tedious and boring to read, but it’s always good to know what you’re getting into. If there’s anything that looks dodgy, it probably is.
-
Before you purchase anything online make sure you’ve read and know your online consumer rights. You can view them here – Which? Online consumer rights.
-
Never click a link in an E-mail that has come from your bank or asks for any login credentials. Banks will never ask for your details over E-mail and very rarely by phone. Treat anything that appears to be from your bank with the utmost caution.
-
Get notified. Make sure you’ve set up any notifications available for online banking. These could be push notifications or text messages with balance updates and more.
Remote Working
-
Since the outbreak of the pandemic, remote working has become prolific. In our rush to get people working from home, security was not given the priority it needed. Download our ultimate guide to securely working from home for our top tips of being secure.
-
Many of us have had to use personal devices in order to get remote working, however, this is not the most secure way of working. While we would always advice to have a dedicated work device, there are a number of steps you can take to safely use your own device, which are listed in our online guide.
- Remote working cybersecurity is important, as many of us plan to work in a hybrid of both office and home based. Always use a VPN when using WiFi outside of the office environment.
Other useful links

-
Educate yourself when it comes to cyber security. The more you understand it the easier you’ll find it to implement effective methods. Our cybersecurity guide for Birmingham businesses is a great starting point, and it's not just about business firewalls.
-
Look at our article on ’25 of the most common used passwords online’. Like the ones above if you use any of these make sure you change them now.
-
Use Bruce Schneier’s password method – This is where you turn a sentence/story into a password. Examples:
I cannot wait to turn 30 in July – 1CntWa2Tu30In07
I like to be at home – Il1k32B@Ho
I went to the shops at work and bought chocolate – 1We2ThSh@Wo&BoC
-
For the full guide about Bruce Schneier’s method read our guide on ‘How to create the perfect password’.
-
When using online banking, it is critical that you have two-factor authentication when logging into your bank account online. You must implement every single security measure when it comes to online banking.
-
Speaking of data breaches take a look at our list of ‘Five biggest cyber attacks in history'. The more you know about cyber security the more likely you are to implement better security yourself.
- Today, cybersecurity supply chains can pose one of the biggest risks, find out about the Kaseya hack to understand how supply chains affects small and large businesses.
-
Check out the cybersecurity website section for more information on cybersecurity.
-
Becoming Cyber Essentials accredited is a great way of becoming cyber secure for any small sized business. Our IASME Cyber Essentials FAQ helps to answer the most common questions about the certification.
- Human error is often one of the biggest threats to a business's cybersecurity. Cyber awareness training can be one of the biggest factors in preventing cyber crime from ever taking place.
- Buying sufficient cybersecurity need not cost a great deal nowadays. Find out the cost of security for a small business in the UK.
- If you want to know what an enhanced cybersecurity for a small business looks like, visit our blog.