Cyber Security Poster
Downloadable cyber security awareness poster Download a free cyber security poster for your office. Educate and remind your team about cyber security...

In an age where wireless connectivity is central to personal and business operations, securing Wi-Fi networks has become a paramount concern.
With the proliferation of Wi-Fi technology, hackers and cybercriminals continually evolve their methods to exploit vulnerabilities in wireless networks. Ensuring the security of a Wi-Fi router thus becomes a critical step in protecting sensitive information from unauthorised access and maintaining the integrity of one's personal and business communications.

Effective Wi-Fi security starts with a fundamental understanding of the technologies and protocols that govern wireless networks, such as Wi-Fi Protected Access (WPA) and the more recent WPA3, which currently provide the highest levels of security.
Beyond these basics, setting up the router with a strong password, changing default settings, and keeping the router's firmware updated are essential practices. However, achieving optimal security demands more than just these initial steps; it requires regularly reviewing and enhancing configurations, monitoring connected devices, and ensuring that both the hardware and software involved in the network setup are up-to-date and secure.

Securing a Wi-Fi router is crucial to safeguarding against cyber threats that target sensitive information and network integrity. This section provides foundational knowledge to bolster router security against common risks.
Secure Wi-Fi routers are the first line of defence in protecting a network. They serve as gatekeepers, safeguarding against unauthorised access and ensuring the confidentiality, integrity, and availability of sensitive information. A compromised router can lead to a plethora of issues, including data breaches and malware dissemination. It is imperative for both individuals and organisations to prioritise router security to prevent hackers from exploiting vulnerabilities for malicious purposes.
Wi-Fi routers face numerous threats that can compromise network security:
To manage these risks, users must:
By understanding and addressing these common router security threats and vulnerabilities, users can significantly reduce the risk of their network being compromised.

Properly setting up one's router is a crucial step to ensuring both access and security for a Wi-Fi network. This section guides users through the initial access to router settings and the configuration of basic security features.
To gain administrative access to a router, one typically needs to log in via a web interface. This generally involves typing the router's IP address into a web browser. The default IP is often 192.168.1.1 or 192.168.0.1. Upon accessing the router's login page, the user will be prompted to enter the default username and password, which is often set as 'admin' for both. However, this information can vary depending on the router's manufacturer and should be changed immediately to prevent unauthorised access.
Default Login Credentials Table:
| Manufacturer | Default IP | Default Username | Default Password |
|---|---|---|---|
| Netgear | 192.168.1.1 | admin | password |
| Linksys | 192.168.1.1 | admin | admin |
| TP-Link | 192.168.0.1 | admin | admin |
| D-Link | 192.168.0.1 | admin | blank |
To find specific instructions for accessing settings on individual devices, users should refer to the router's user manual or official website.
Once inside the router's settings, the user should primarily focus on establishing a strong password and setting up the Service Set Identifier (SSID). It's vital that they replace factory preset passwords with robust, unique passwords to fortify their network against breaches.
For enhanced security, users should ensure that their network is encrypted with Wi-Fi Protected Access 2 (WPA2) or Wi-Fi Protected Access 3 (WPA3) security protocol. In the router's security settings, select the appropriate protocol and create a passphrase, effectively encrypting the network traffic.
Users should be aware that manufacturers periodically release firmware updates that may include vital security enhancements. It is recommended to check for updates regularly and apply them to maintain the router's security integrity.
Experts agree that enhancing the security of a Wi-Fi router often requires more than just basic setup; it necessitates advanced configuration that safeguards the network against sophisticated threats.
Firmware is the foundational software that controls the router. Regular firmware updates are critical as they can fix known security vulnerabilities and offer new security features. Router manufacturers periodically release firmware updates, which should be applied promptly to ensure the highest level of security. Users can often set routers to update their firmware automatically, ensuring the latest protections are always in place.
Wireless encryption is a mechanism that protects the data travelling over a Wi-Fi network. Routers should be configured to use the most advanced form of encryption available to them. For the majority of current routers, WPA2 (Wi-Fi Protected Access 2) or WPA3 offer strong encryption standards. WPA3, being the latest, provides improved security features over WPA2, including Advanced Encryption Standard (AES) support, which is robust against attacks. Using obsolete standards like WEP (Wired Equivalent Privacy) is strongly discouraged as they offer minimal protection against modern attack methods. By selecting the strongest encryption setting available, the Wi-Fi network becomes significantly more secure against unauthorised access and eavesdropping.
To safeguard Wi-Fi networks effectively, it's crucial to enhance security parameters governing network access. This includes setting robust login credentials and employing mechanisms such as MAC filtering to manage device connectivity.
Strong login credentials are the first line of defence. Router owners should create a strong password that combines uppercase and lowercase letters, numbers, and special characters. It’s advised to avoid common words or easily guessable combinations. Using a password manager can help in generating and storing complex passwords securely. Here's an example of a strong password structure:
The login details for router access should be distinct from other credentials used within one's personal or professional sphere to mitigate the risk in case of a security breach elsewhere.
MAC filtering adds an extra security layer by controlling which devices can connect to the network. Each device has a unique Media Access Control (MAC) address that can be used to grant or deny network access. To implement MAC filtering:
Here's a simplified process to manage MAC filtering:
By controlling device connectivity through MAC filtering, network owners can prevent unauthorised access, strengthening their Wi-Fi security posture.
To protect a Wi-Fi network, it is essential to implement robust security protocols that go beyond the basic settings. Routers should be configured to use advanced encryption standards like WPA2 or, preferably, WPA3 to safeguard data integrity and user privacy.
Modern routers are equipped with built-in firewalls that control the incoming and outgoing network traffic based on predetermined security rules. The activation of these firewalls contributes to preventing unauthorised access and various forms of cyberattacks. It’s crucial to regularly update the firewall’s security settings to ensure the highest level of network protection.
Alongside firewalls, Universal Plug and Play (UPnP) allows networked devices to discover each other’s presence seamlessly. However, UPnP can be exploited by malicious actors if not properly secured. Therefore, UPnP settings should be carefully configured, or disabled if not needed, to avoid potential security vulnerabilities.
Creating a separate network for guests helps to isolate the main network from potential security breaches.
By implementing these practices, network administrators can significantly enhance the security of their Wi-Fi networks.
Enhancing the security of a Wi-Fi router involves adopting methods that protect both the network and its remote access points. Specifically, the use of Virtual Private Networks (VPNs) and the deactivation of Wi-Fi Protected Setup (WPS) provides robust layers of security.
A Virtual Private Network (VPN) establishes a protected network connection when using public networks. VPNs encrypt data, ensuring that a remote user's online actions remain private and untraceable. It is imperative for individuals and businesses to utilise a VPN to safeguard their remote access to the Wi-Fi network, thereby preventing unauthorised interception of sensitive information.
Wi-Fi Protected Setup (WPS) offers a convenient method for connecting devices to a network without entering a password. However, this feature can also be vulnerable to external attacks, making the network susceptible to unauthorised access. Security experts recommend disabling WPS on routers, compelling users to connect only through more secure, manual authentication processes. This simple step significantly enhances the router's protection against potential breaches.
To maintain robust Wi-Fi router security, it is crucial to have a system in place for monitoring and controlling which devices are connected to your network.
Routinely checking the list of gadgets that are attached to your Wi-Fi network is an essential step in enhancing security. Every device that is connected will have an assigned IP address which can be viewed in the router's administrative console. This regular review helps one verify that all devices are recognised and authorised. Owners should be alert for unknown devices and should consult the device's MAC address or interface name to identify unfamiliar gadgets.
Owners should:
Implementing controls to limit unwarranted access to your Wi-Fi network increases the security level significantly. Utilising features such as MAC address filtering adds a layer of control, permitting only known devices to connect. One can further enhance security by disabling WPS (Wi-Fi Protected Setup), which is known to have vulnerabilities, and by changing the router's default admin credentials to prevent unauthorised configuration.
Steps to control device connections:
By adhering to these methods, one can help secure their Wi-Fi routers from unauthorised devices and potential security threats.
Securing personal and sensitive information over Wi-Fi networks is critical to prevent unauthorised access and potential data breaches. A user must employ robust security measures to ensure that any transmission of private data across their network remains confidential and secure.
When sharing sensitive data over a network, it's essential to utilise encryption protocols such as WPA3 or, at the very least, WPA2. These protocols ensure that the data remains incomprehensible to anyone who might intercept it. Furthermore, individuals should use VPN services to create a secure tunnel for data passage, notably when connecting to public Wi-Fi networks. This adds an extra layer of security, encrypting data traffic from a device through to the VPN server.
Table: Recommended Encryption Protocols
| Protocol | Security Level | Compatibility |
|---|---|---|
| WEP | Low | High |
| WPA | Medium | Moderate |
| WPA2 | High | Moderate |
| WPA3 | Very High | Emerging |
One of the common errors that users make is failing to change default passwords on their Wi-Fi routers. Attackers often exploit these default credentials to gain access to the network. Users should replace default passwords with strong, unique passwords and regularly update firmware to patch any security vulnerabilities. Additionally, disabling features not in use, like Remote Management and WPS (Wi-Fi Protected Setup), can significantly reduce the risk of unauthorised access to one's private data. Regular network monitoring for unauthorised devices and disabling broadcasting of the network SSID will also enhance the security of sensitive information.
Always:
Never:
Maintaining optimised security requires regular attention to two critical aspects: security audits and the application of updates. Organisations must schedule these activities to identify vulnerabilities and apply necessary updates proactively.
It is imperative for companies to implement regular security audits to assess the resilience of their Wi-Fi networks. These audits should consist of:
Regular audits offer foresight into potential security threats, allowing organisations to rectify issues before they are exploited. These assessments are best conducted by a security expert, either in-house or from an outside firm, who is well-versed in the latest threats and defence mechanisms.
Wi-Fi routers require the latest security patches and firmware updates to defend against new vulnerabilities. Organisations must:
By continuously applying the latest patches and updates, companies can protect their Wi-Fi networks from the latest threats. Firmware updates may contain crucial security enhancements that bolster the network's defences, ensuring that private data remains secure.
When setting up a Wi-Fi network, the security of one's data and devices hinges on selecting appropriate hardware and software. It's vital to choose routers and accessories with robust security features and pair these with effective antivirus software to safeguard against threats.
Selecting the right make and model of router is crucial for a secure Wi-Fi network. One needs to look for devices that offer advanced security features such as WPA3 encryption, the ability to create guest networks, and the option for firmware updates. For instance, routers from reputable brands like Netgear, Asus, or Cisco often come with these enhanced security measures.
Here is a simple table outlining key security features to consider:
| Feature | Description |
|---|---|
| WPA3 Encryption | The latest security protocol for Wi-Fi networks, providing improved data protection. |
| Guest Networks | Allows the creation of separate access for guests, keeping the main network more secure. |
| Firmware Updates | Regular updates can fix vulnerabilities and enhance the router's security. |
| VPN Support | Offers the ability to set up a Virtual Private Network, securing remote access to the network. |
| Firewalls | In-built hardware or software designed to block unauthorised access to the network. |
Moreover, additional accessories like hardware firewalls or network security gateways can provide an extra layer of protection. These are particularly important for businesses or scenarios where sensitive data is frequently transmitted across the network.
Antivirus software plays a pivotal role in protecting against malware that could compromise a Wi-Fi network. It's essential for both individual devices and the network as a whole. When selecting antivirus software, one should opt for reputable solutions known for their ability to detect and neutralise threats effectively.
For example, antivirus programs from companies like Norton, McAfee or Kaspersky offer real-time protection against a plethora of cyber threats, including viruses, worms, trojans, and ransomware. They may also include features such as:
By carefully considering both the hardware and software aspects of a Wi-Fi network, users can significantly improve the security and integrity of their data transmission and prevent unauthorised access or attacks.
Securing a home WiFi router is critical to prevent unauthorised access and protect against cyber threats. The following FAQs address common concerns and provide specific actions for enhancing WiFi security.
One should change default usernames and passwords, update the router's firmware, and disable any remote management features. It's also wise to change the network's default SSID to something non-identifiable.
Regularly updating passwords, using a robust encryption method like WPA3, and turning off WPS are key practices. One should also monitor connected devices and consider using a network firewall.
By accessing the router's web interface, users can enable network encryption, create a guest network with separate access, and implement MAC address filtering to allow only recognised devices on the network.
Passwords should be complex, comprising a mix of letters, numbers, and symbols. Avoiding common words and regularly updating the password significantly increase the network's security.
Wi-Fi Protected Access 3 (WPA3) is currently the most secure protocol, providing stronger encryption and better protection against brute-force attacks than its predecessors, WPA2 and WEP.
Users should consider employing advanced security features like VPNs for secure remote access, implementing strong encryption protocols, and regularly auditing their network for vulnerabilities.
Implementing security measures takes time, but the long-term investment is worthwhile. Improving your overall resilience will reduce the number of business disruptions and the damage they cause. Get in touch to understand what security measures are proportionate for your business size.
Grade your organizational risk with our comprehensive cybersecurity quiz.
🎯 Grade Your Organizational Risk: CLICK HERE
================================
Our quiz is more than just a set of questions; it's a window into your organization's cybersecurity posture. By participating, you're not just testing your knowledge; you're evaluating your organization's readiness against cyber threats.
As your trusted MSP, we're committed to helping you navigate the complex world of cybersecurity. This quiz is the first step in a journey towards a more secure digital environment for your business.
Take the Quiz Now and pave the way for a safer digital future for your organization. Remember, in the realm of cybersecurity, knowledge is not just power – it's protection.
👉 DON'T WAIT FOR A BREACH TO REALIZE THE IMPORTANCE OF CYBERSECURITY.
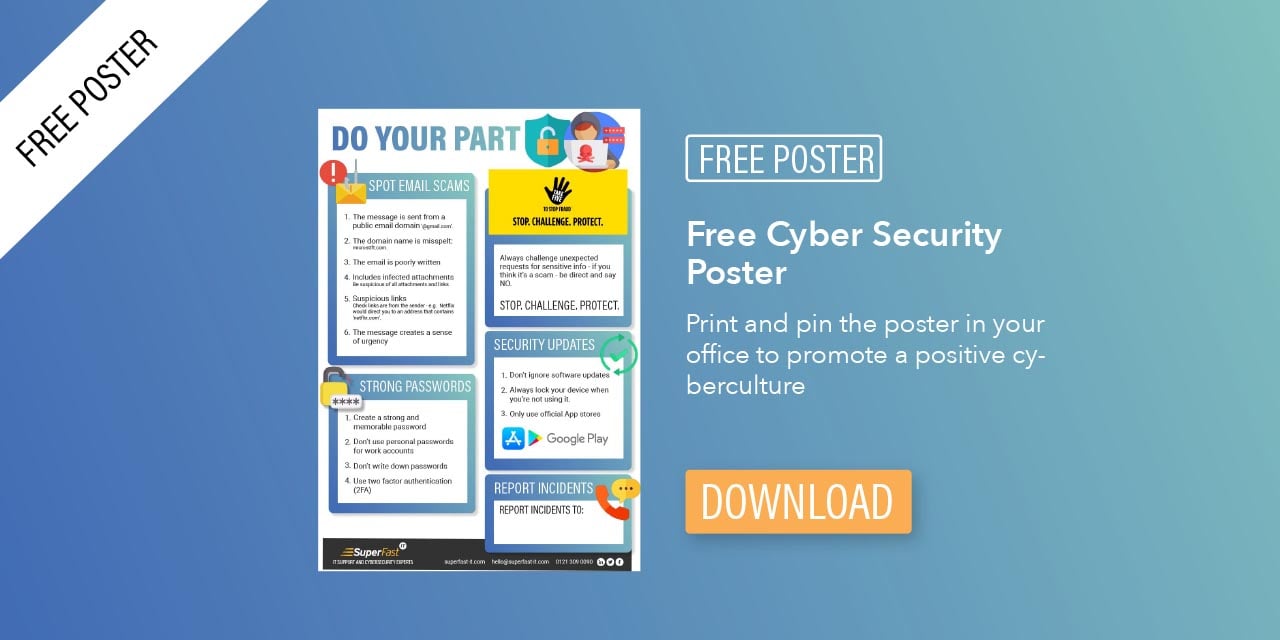
Downloadable cyber security awareness poster Download a free cyber security poster for your office. Educate and remind your team about cyber security...

Many businesses turn to their IT company to help them pass Cyber Essentials accreditation. The National Cyber Security Centre (NCSC) recently...

James explains what is included in our Enhanced Security Package in the video below: {% video_player "embed_player" overrideable=False,...